AIStore + HuggingFace: Distributed Downloads for Large-Scale Machine Learning
AIStore + HuggingFace: Distributed Downloads for Large-Scale Machine Learning
Machine learning teams increasingly rely on large datasets from HuggingFace to power their models. But traditional download tools struggle with terabyte-scale datasets containing thousands of files, creating bottlenecks that slow development cycles.
This post introduces AIStore’s new HuggingFace download integration, which enables efficient downloads of large datasets with parallel batch jobs.
Table of contents
- Background
- CLI Integration: Simplified Workflows
- Download Optimizations
- Complete Walkthrough: NonverbalTTS Dataset
- Next Steps
- Conclusion
Background
Sequential downloads create significant bottlenecks when dealing with complex datasets that have hundreds of thousands of files distributed across multiple directories.
AIStore addresses this by parallelizing downloads within each target using multiple workers (one per mountpath), batching jobs based on file size, and collecting file metadata in parallel. This approach leverages the network throughput from each individual target to the HuggingFace servers.
CLI Integration: Simplified Workflows
Prerequisites
The following examples assume an active AIStore cluster. If the destination buckets (e.g., ais://datasets, ais://models) don’t exist, they will be created automatically with default properties.
AIStore’s CLI includes HuggingFace-specific flags for the ais download command that handle distributed operations behind the scenes.
Basic Download Commands
# Download entire dataset
$ ais download --hf-dataset squad ais://datasets/squad/
# Download entire model
$ ais download --hf-model bert-base-uncased ais://models/bert/
# Download specific file
$ ais download --hf-dataset squad --hf-file train/0.parquet ais://datasets/squad/
Authentication and Configuration
# Export your HuggingFace token and use for private/gated content
$ export HF_TOKEN=your_hf_token_here
$ ais download --hf-dataset private-dataset --hf-auth $HF_TOKEN ais://private-data/
# Control batching with blob threshold
$ ais download --hf-dataset large-dataset --blob-threshold 200MB ais://datasets/large/
Progress Monitoring
# Real-time progress tracking
$ ais show job --refresh 2s
# Detailed job information
$ ais show job download --verbose
Download Optimizations
The system uses some key techniques to improve download performance:
Job Batching: Size-Based Distribution
Job batching categorizes files based on configurable size thresholds:
# Configure blob threshold for job batching
$ ais download --hf-dataset squad --blob-threshold 100MB ais://ml-datasets/
Files are categorized into two groups:
- Large files (above blob threshold): Get individual download jobs for maximum parallelism
- Small files (below threshold): Batched together to reduce overhead
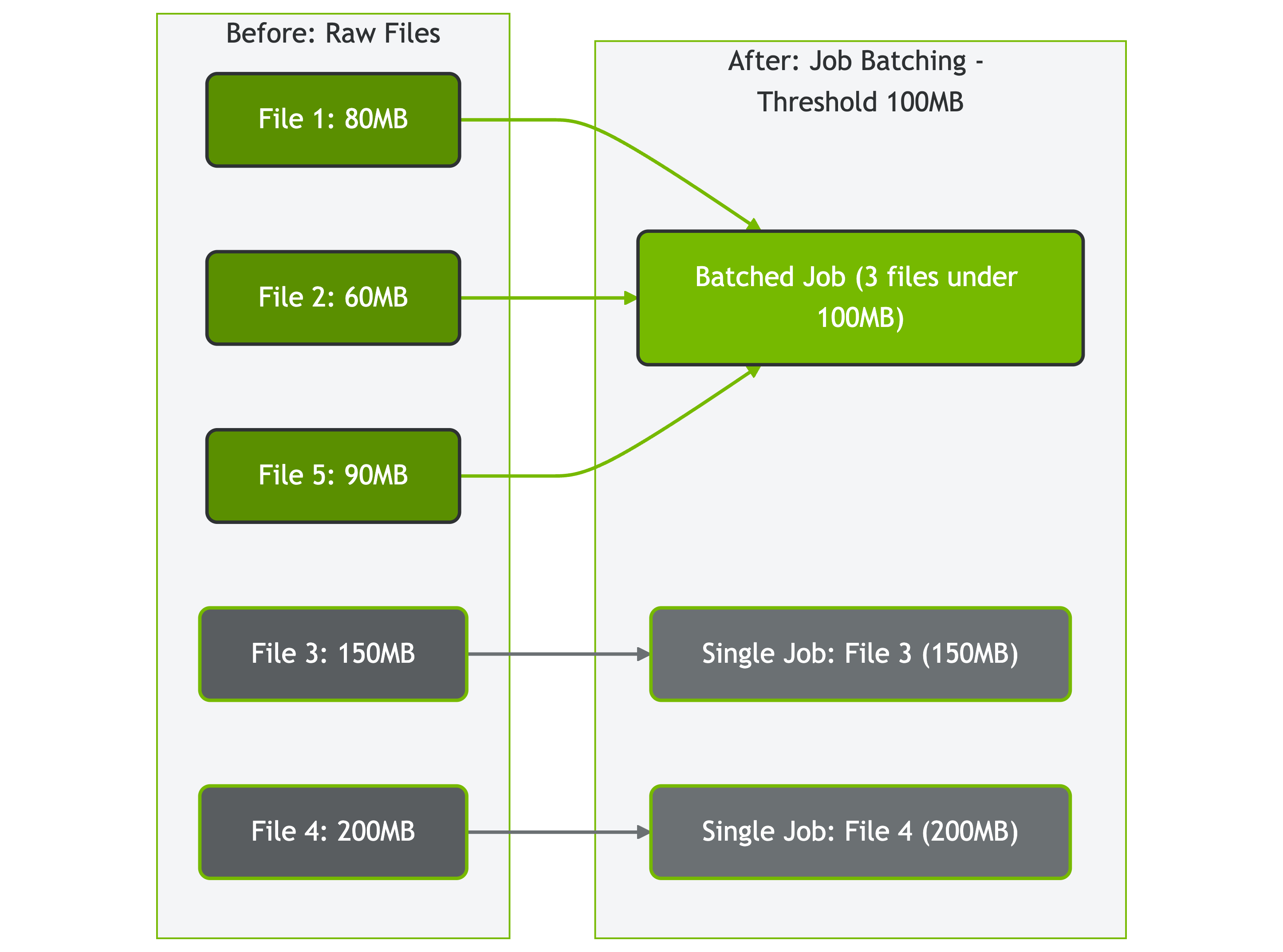 Figure: How AIStore batches files based on size threshold (100MB in this example)
Figure: How AIStore batches files based on size threshold (100MB in this example)
Concurrent Metadata Collection
Before downloading files, AIStore makes parallel HEAD requests to the HuggingFace API to collect file metadata (like file sizes) concurrently rather than sequentially. This reduces setup time for datasets with many files.
Complete Walkthrough: NonverbalTTS Dataset
Let’s walk through an example downloading a machine learning dataset and processing it with ETL operations:
Walkthrough Prerequisites
For this walkthrough, we’ll create and use three buckets:
ais://deepvs- for the initial dataset downloadais://ml-dataset- for ETL-processed filesais://ml-dataset-parsed- for the final parsed dataset
If these buckets don’t exist, they will be created automatically with default properties.
Step 1: Download Dataset with Configurable Job Batching
# Download deepvk/NonverbalTTS dataset with job batching
$ ais download --hf-dataset deepvk/NonverbalTTS ais://deepvs --blob-threshold 500MB --max-conns 5
Found 11 parquet files in dataset 'deepvk/NonverbalTTS'
Created 7 individual jobs for files >= 500MiB
Started download job dnl-B-oOHruKH9
To monitor the progress, run 'ais show job dnl-B-oOHruKH9 --progress'
Step 2: Monitor Distributed Job Execution
# Watch configurable job distribution across cluster targets
$ ais show job
download jobs
JOB ID XACTION STATUS ERRORS DESCRIPTION
dnl-B-oOHruKH9 D6JOGa7PH9 1 pending 0 multi-download -> ais://deepvs
dnl-zoOHr7PG3 D6JOGa7PH9 1 pending 0 https://huggingface.co/api/datasets/deepvk/NonverbalTTS/parquet/default/other/0.parquet -> ais://deepvs/0.parquet
dnl-oJOHruKG3 D6JOGa7PH9 1 pending 0 https://huggingface.co/api/datasets/deepvk/NonverbalTTS/parquet/default/train/1.parquet -> ais://deepvs/1.parquet
dnl-F_ogHauKH9 D6JOGa7PH9 1 pending 0 https://huggingface.co/api/datasets/deepvk/NonverbalTTS/parquet/default/train/2.parquet -> ais://deepvs/2.parquet
dnl-PoOHr7KG9 D6JOGa7PH9 1 pending 0 https://huggingface.co/api/datasets/deepvk/NonverbalTTS/parquet/default/train/3.parquet -> ais://deepvs/3.parquet
....
Step 3: Verify Download Completion
# Check bucket summary after download
$ ais ls ais://deepvs --summary
NAME PRESENT OBJECTS SIZE (apparent, objects, remote) USAGE(%)
ais://deepvs yes 6 0 2.76GiB 2.76GiB 0B 0%
Options for Using Downloaded Data
At this point, you have several options:
- Use directly: Work with the downloaded files as-is if they meet your requirements
- Transform with ETL: Apply preprocessing for format conversion, file organization, or data standardization
- Custom processing: Use your own tools for data preparation
Why transform? HuggingFace datasets often have complex paths or formats that benefit from standardization. This walkthrough demonstrates ETL transformations for file organization (consistent naming) and format conversion (Parquet → JSON for framework compatibility).
Step 4: Initialize ETL Transformers
Note: ETL operations require AIStore to be deployed on Kubernetes. See ETL documentation for deployment requirements and setup instructions.
Before applying transformations, initialize the required ETL containers:
# Initialize batch-rename ETL transformer for file organization
$ ais etl init -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/NVIDIA/ais-etl/main/transformers/batch_rename/etl_spec.yaml
# Initialize parquet-parser ETL transformer for data parsing
$ ais etl init -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/NVIDIA/ais-etl/main/transformers/parquet-parser/etl_spec.yaml
# Verify ETL transformers are running
$ ais etl show
Step 5: Preprocessing using ETL
# Organize and rename files using batch rename ETL
$ ais etl bucket batch-rename-etl ais://deepvs ais://ml-dataset
etl-bucket[BatchRename] ais://deepvs => ais://ml-dataset
# Verify renamed files with structured naming
$ ais ls ais://ml-dataset/
NAME SIZE
train_0.parquet 485MiB
train_1.parquet 492MiB
train_2.parquet 511MiB
...
# Convert parquet files to JSON format for easier ML framework integration
$ ais etl bucket parquet-parser-etl ais://ml-dataset ais://ml-dataset-parsed
etl-bucket[xO_sVT3Im] ais://ml-dataset => ais://ml-dataset-parsed
# Verify processed dataset ready for ML training
$ ais ls ais://ml-dataset-parsed --summary
NAME PRESENT OBJECTS SIZE (apparent, objects, remote) USAGE(%)
ais://ml-dataset-parsed yes 7 0 8.68GiB 8.68GiB 0B 1%
Step 6: ML Pipeline Integration
AIStore integrates seamlessly with popular ML frameworks. Here’s how to use the processed dataset in your training pipeline:
Option A: Direct SDK Usage (Simple)
from aistore.sdk import Client
import json
client = Client("http://localhost:51080")
bucket = client.bucket("ml-dataset-parsed")
# Load processed training data
for obj in bucket.list_objects():
if obj.name.startswith("train_"):
data = json.loads(obj.get_reader().read_all())
# Process individual training samples
for sample in data:
# Your training logic here
pass
Option B: PyTorch Integration (Recommended for ML Training)
from aistore.sdk import Client
from aistore.pytorch import AISIterDataset
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import json
# Create dataset that reads directly from the cluster
client = Client("http://localhost:51080")
dataset = AISIterDataset(ais_source_list=client.bucket("ml-dataset-parsed"))
# Configure DataLoader with multiprocessing
loader = DataLoader(
dataset,
batch_size=32,
num_workers=4, # Parallel data loading across multiple cores
)
# Training loop
for batch_names, batch_data in loader:
# Parse JSON data
parsed_samples = [json.loads(data) for data in batch_data]
# Convert to tensors and train your model
# model.train_step(parsed_samples)
pass
Next Steps
The HuggingFace integration opens up some practical areas for expansion:
Download and Transform API: AIStore supports combining download and ETL transformation in a single API call, eliminating the two-step process shown in the walkthrough. This allows downloading HuggingFace datasets with immediate transformation (e.g., Parquet → JSON) in one operation. CLI integration for this functionality is in development.
Additional Dataset Formats: Beyond the current Parquet support, HuggingFace datasets are available in multiple formats that teams commonly need:
- JSON format - Direct JSON downloads for frameworks requiring this format
- CSV format - For traditional data processing workflows
- WebDataset format - For large-scale ML pipelines using WebDataset
Conclusion
AIStore’s HuggingFace integration addresses common dataset download bottlenecks in machine learning workflows. Job batching and concurrent metadata collection enable efficient, parallel downloads of terabyte-scale datasets that would otherwise overwhelm traditional tools. Once stored in AIStore, teams can leverage local ETL operations to transform and prepare data without additional network transfers. This approach provides a streamlined path from raw downloads to training-ready datasets, eliminating the typical download-wait-process cycle that slows ML development.
References:
AIStore Core Documentation
- AIStore GitHub
- AIStore Blog
- AIStore Downloader Documentation
- AIStore Python SDK
- AIStore PyTorch Integration - High-performance data loading for ML training
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) Resources
- ETL Documentation - Comprehensive guide to AIStore ETL capabilities and Kubernetes deployment
- ETL CLI Reference - Command-line interface for ETL operations
- Batch-Rename Transformer - File organization and renaming
- Parquet Parser Transformer - Parquet to JSON conversion
- AIStore Kubernetes Deployment - Production Kubernetes deployment tools and documentation
External Resources

