ETL IMAGENET PYTORCH
PyTorch ImageNet preprocessing with ETL
In this example, we will see how to use ETL to preprocess the images of ImageNet which then can be used for training.
Note: ETL is still in development so some steps may not work exactly as written below.
Overview
This tutorial consists of couple steps:
- Prepare AIStore cluster.
- Prepare dataset.
- Prepare transform code (ETL).
- Transform dataset on AIStore cluster with ETL.
Here is a general overview of these steps:
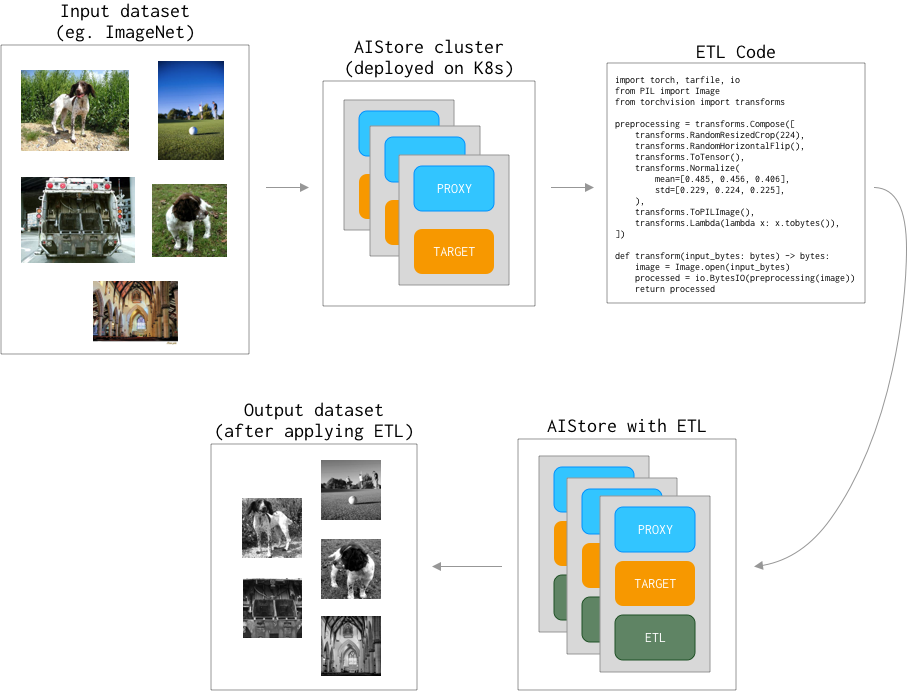
Prerequisites
- AIStore cluster deployed on Kubernetes. We recommend following guide: Deploy AIStore on local Kubernetes cluster
Prepare dataset
Before we start writing code, let’s put an example tarball file with ImageNet images to the AIStore.
The tarball we will be using is n02085620.tar (saved as raw-train.tar) from ILSVRC2012_img_train_t3.tar.
$ tar -tvf raw-train.tar | head -n 5
-rw-r--r-- 0 aditya86 users 27024 Jul 4 2012 n02085620_10074.JPEG
-rw-r--r-- 0 aditya86 users 34446 Jul 4 2012 n02085620_10131.JPEG
-rw-r--r-- 0 aditya86 users 12891 Jul 4 2012 n02085620_10621.JPEG
-rw-r--r-- 0 aditya86 users 34837 Jul 4 2012 n02085620_1073.JPEG
-rw-r--r-- 0 aditya86 users 18126 Jul 4 2012 n02085620_10976.JPEG
$ ais create ais://imagenet
"ais://imagenet" bucket created
$ ais put raw-train.tar imagenet
PUT "raw-train.tar" into bucket "imagenet"
Prepare ETL code
As we have ImageNet prepared now we need an ETL code that will do the transformation.
Here we will use python3 runtime to install the torchvision package.
Our transform code will look like this (code.py):
import tarfile, io
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
def img_to_bytes(img):
buf = io.BytesIO()
img = img.convert('RGB')
img.save(buf, format='JPEG')
return buf.getvalue()
preprocessing = transforms.Compose([
transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]),
transforms.ToPILImage(),
transforms.Lambda(img_to_bytes),
])
def transform(input_bytes: bytes) -> bytes:
input_tar = tarfile.open(fileobj=io.BytesIO(input_bytes))
output_bytes = io.BytesIO()
output_tar = tarfile.open(fileobj=output_bytes, mode="w|")
for member in input_tar:
image = Image.open(input_tar.extractfile(member))
processed = preprocessing(image)
member.size = len(processed)
output_tar.addfile(member, io.BytesIO(processed))
output_tar.close()
return output_bytes.getvalue()
The idea here is that we unpack the tarball, process each image and save it into transformed output tarball.
To make sure that the code runs we need to specify required dependencies (deps.txt):
torchvision==0.15.1
Transform dataset
Now we can build the ETL:
$ ais etl init code --from-file=code.py --deps-file=deps.txt --runtime=python3.11v2 --name="pytorch-transformer" --comm-type hpull
pytorch-transformer
$ ais etl object pytorch-transformer imagenet/raw-train.tar preprocessed-train.tar
$ tar -tvf preprocessed-train.tar | head -n 5
-rw-r--r-- 0 aditya86 users 150528 Jul 4 2012 n02085620_10074.JPEG
-rw-r--r-- 0 aditya86 users 150528 Jul 4 2012 n02085620_10131.JPEG
-rw-r--r-- 0 aditya86 users 150528 Jul 4 2012 n02085620_10621.JPEG
-rw-r--r-- 0 aditya86 users 150528 Jul 4 2012 n02085620_1073.JPEG
-rw-r--r-- 0 aditya86 users 150528 Jul 4 2012 n02085620_10976.JPEG
As expected, the size of the new tarball images has been standardized as all images have the same resolution (224*224*3=150528).

